Re-Design a Bone Densitometry Device
Based on Two Different Design Method
(Authors: Kiarash Rahayi, Sana Behnam)
In this university project, we were asked to redesign a subject based on two different design methods. Our chosen topic had a lot of initial studies, both in terms of patient-related topics and hardware-related topics. These studies clarified why the device has been designed in this way so far and what the design limitations will be.
On the other hand, some of these initial studies were applicable to both methods and some were not. This allowed the studies to expand beyond what was expected. In this summary, more important sections are given. Those sections that had the greatest impact on the final design, and sections of the initial study, were often omitted to avoid prolonging this summary.
Foreword
Despite its hard and strong appearance, bone is a living organ that is composed of a combination of biological substances such as collagen and non-biological substances called hydroxyapatite along with blood vessels and the nervous system. But the purpose of reducing or increasing bone density is to change the amount of calcium or hydroxyapatite inside the bone. In postmenopausal women or certain diseases due to biological reasons, this mass is low density and threatens the health of people in terms of fractures and disability. Osteoporosis has no warning signs and patients usually have no symptoms until the bones break. The main symptom of osteoporosis is the main complication, ie fracture. For this reason, people who feel this risk should have their bone density measured in specific areas, such as the femoral neck and the vertebrae at the end of the spine, and compared with healthy people and their peers.
Introduction
One of the most accurate and widely used methods of bone densitometry is the Dexa method. This non-invasive and painless method can measure bone density loss in a short time between one to ten minutes (less than half an hour) depending on the device. This method is often used to diagnose osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and sometimes in men, as well as to determine the risk of bone fractures. Dexa can be used to follow the treatment of osteoporosis.
There are dual energy x-rays with two distinct peaks, one absorbed mainly by soft tissue and the other by bone. The difference between the total amount and the amount absorbed by the soft tissue determines the density of the bone tissue.
The type of device we chose was the central Dexa, which consists of a large table and bed with arms and is used to measure the density of the pelvic bones and spine.
The advantages of Dexa include the following:
• Dexa densitometry is simple, fast, non-invasive and painless.
• No local or complete anesthesia is required to perform the test.
• The amount of radiation in this test is very low.
the pelvis test position
the spine test position

DEXA analyze and result
the first method: rational method of Nigel Cross
In his book, Design Engineering, Nigel Cross discusses the logical design method, arguing that logical methods have similarities in their path with creative methods, such as expanding the space for potential solutions, or facilitating teamwork and group decision-making.
After introducing this method, he proposes seven stages for its realization. However, he believes that these stages and their details should not be considered as immutable constants.
The design method includes the following steps (shown in the chart below): Clarifying objectives, Establishing functions, Setting requirements, Determining characteristics, Generating alternatives, Evaluating alternatives, Improving details

Seven stages of the design process positioned within the symmetrical problem/ solution model
Objectives Tree
In this section, the main issues required in the design are discussed. For this reason, the same classification has been done in relation to the bone densitometery. The main topics related to the product are categorized in the "Objectives Tree" and the sub-categories of each section are expanded as much as possible.

Objectives Tree with connection between different section (with dash-line)
Function Analysis
In this section, the main functions and range of the system are considered and it is determined in what range of general and partial performance the product is. At this stage, the main function that the product should achieve is determined by research and interview with the employer and there is no reference to how to achieve it. Also, these functions in relation to the densitometer are shown in the following figures. After the main function is specified, more detailed functions are specified. Also, in this step, the inputs and transactions between the minor functions are specified and the general scope of functions in the system is determined.
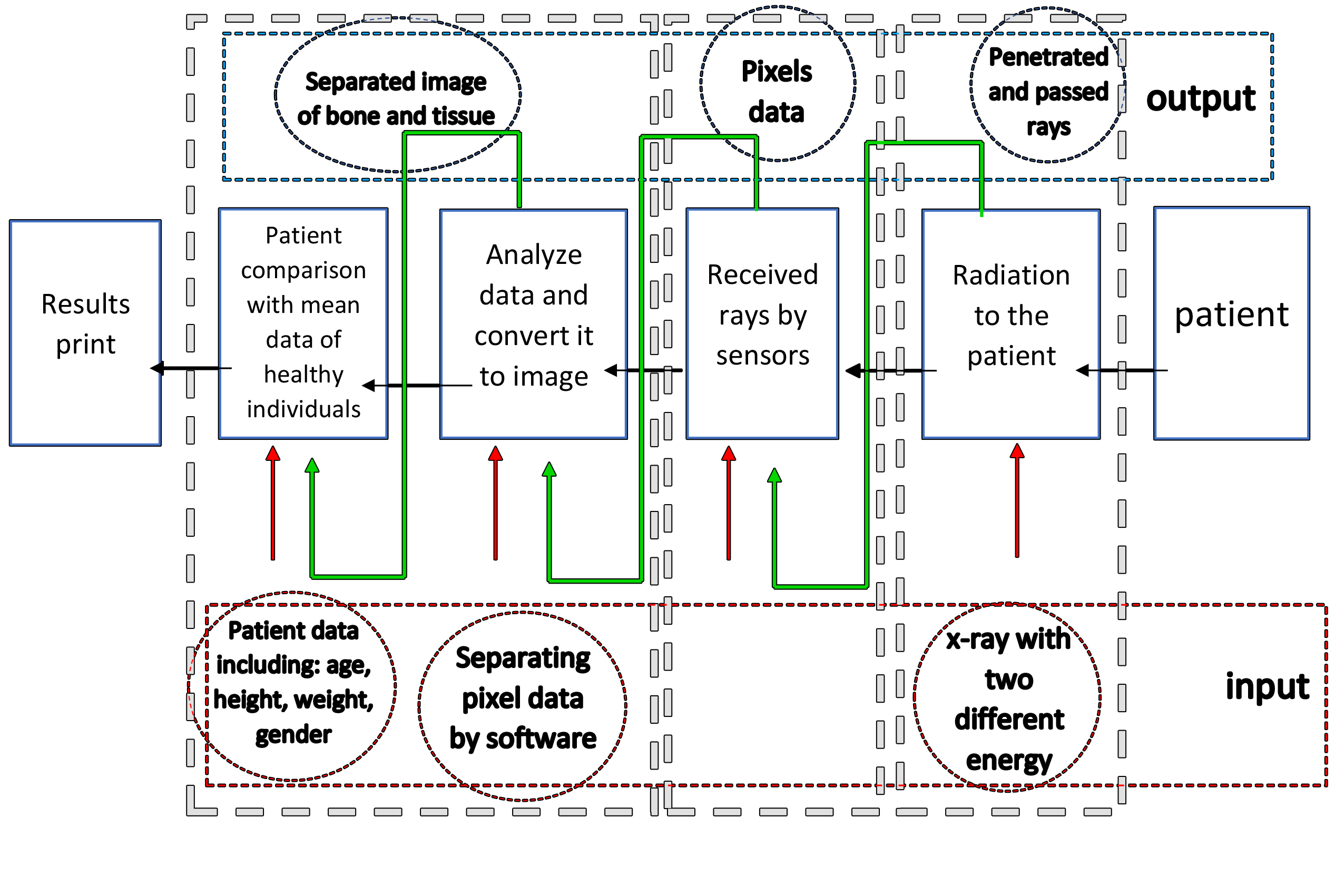
the range of the system and its input and output in different stages of operation are specified
The Voice of Costumer and House of Quality
At this stage, we generally identify, categorize and evaluate the needs of users based on the customer's voice and the information obtained from interviews or questions from users and experts. Also, executive features and suitable solutions for each need are suggested.
It should be said that the main purpose of identifying the needs of the user is to relate it to technical features and practical solutions. Then, the section of product samples available in the market and the features available in this product are examined. Also, the performance of each competing product (Discovery, Explorer, Delphi, QDR) in relation to the customer's voice and the mentioned needs are measured.
And then the executive needs and technical solutions that can meet the needs of the user are examined. In this section, the relationships between these solutions are also examined and the degree of direct or inverse of these factors with each other is also measured.
In the following, the relationships between users' needs and parameters and technical solutions are discussed and the relationship between these parameters and needs is measured at three levels: strong, medium and weak. In the final part of the QFD stage, the final criteria are measured and it is determined to what extent these criteria can meet the mentioned needs, as well as new goals for new product design are presented.
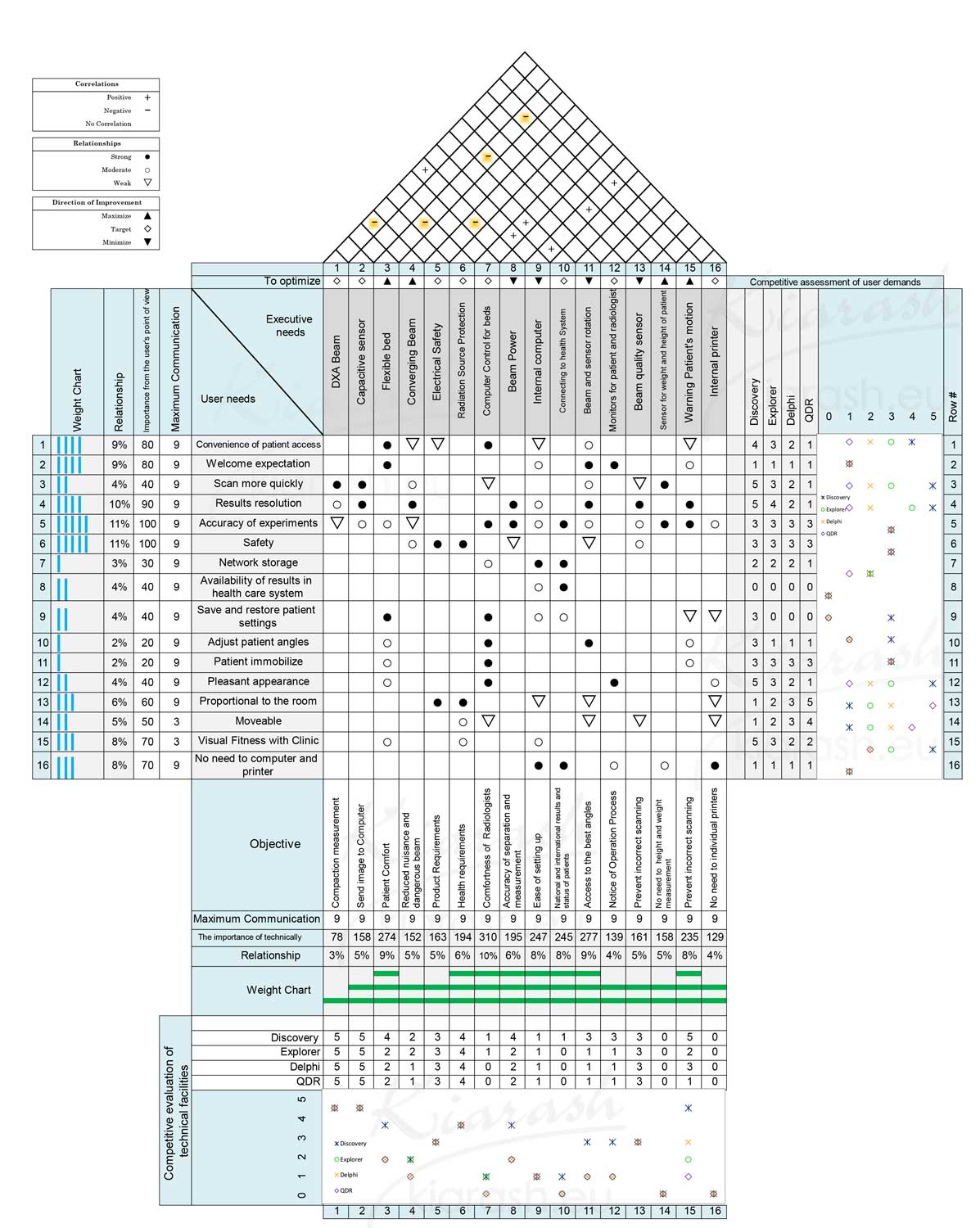
the House of Quality
Provide New Solutions Based on Goals
At this stage, various solutions are provided for each of the goals and different modes of the proposed solutions are considered. design criteria are scored based on their relationship to each other. Their relationship is determined by 1 (related) and 0 (unrelated).
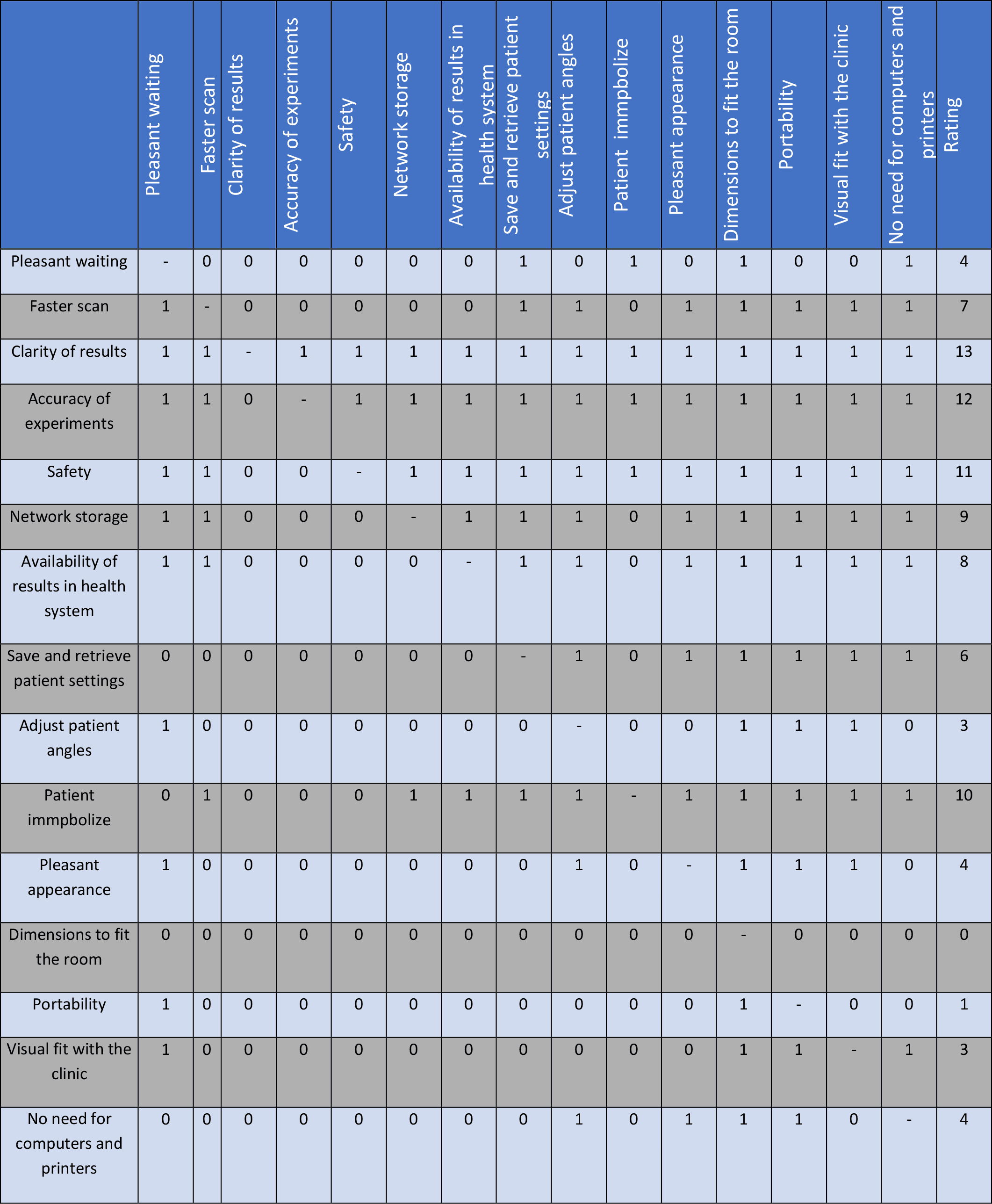
Score design criteria
In the final section, each of the design criteria is evaluated. Finally, the solution that provides the most points (according to the considered values) is selected as the best design.In the end, it is sketched based on the alternatives and selected designs, and the best option is selected as the selected design.

Results of evaluation of design criteria
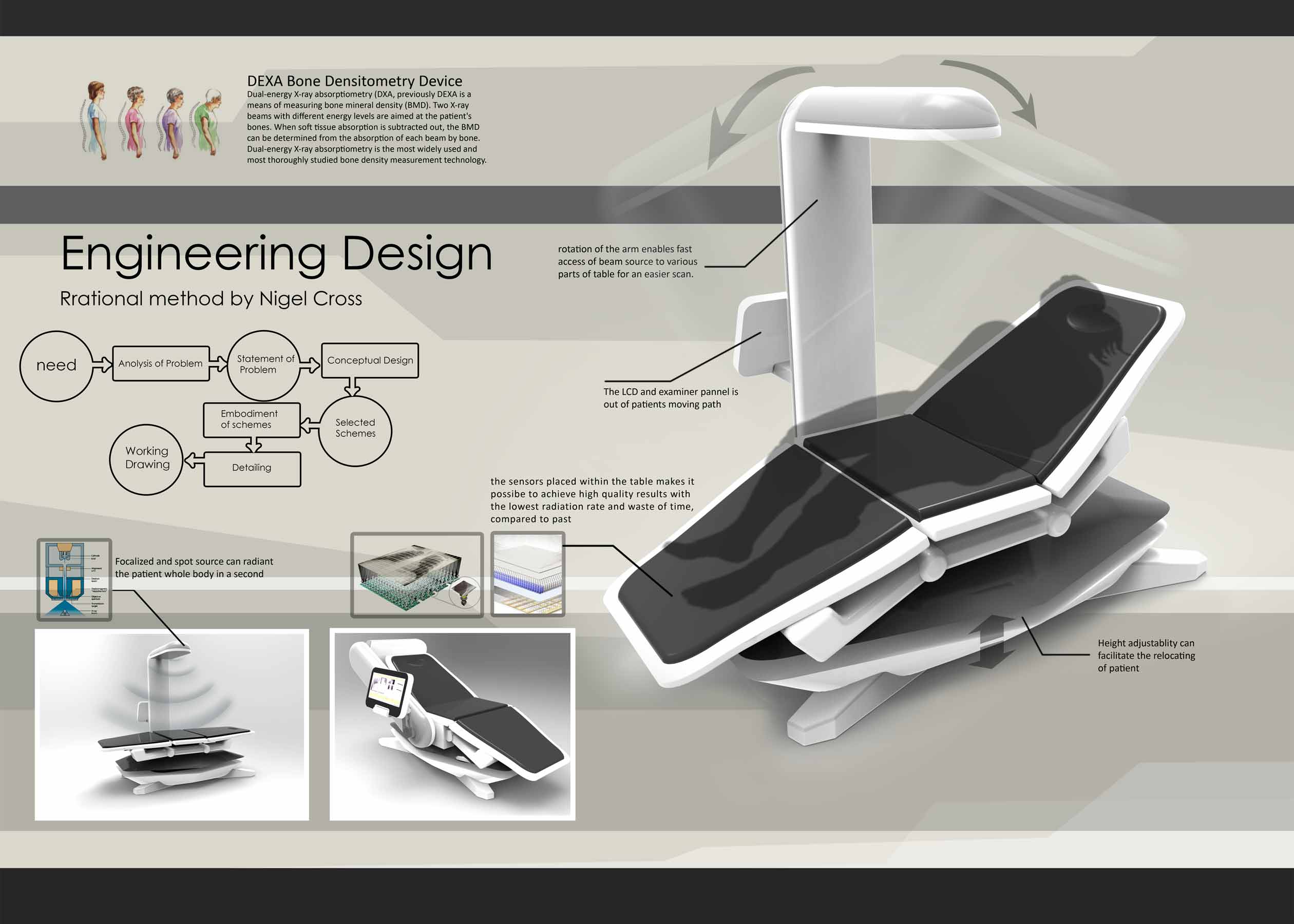
the Final Design
The Second Method: Kansei Engineering (emotional/affective)
Japanese publishers have published various versions of models used by Kansei Engineering in various products. The model of this project is based on the studies of Simon Schütte (Faculty of Management and Engineering at Linköping University, Sweden), which was also published in the journal Quality Management "TQM" in 2008.
First, a general map of the process of this method is drawn and it is determined what characteristics the different parts of this method have and in what order the steps of this method should be done. The following figure shows the outline of the method ahead.

Simon Schütte kansei engineering model
Spanning the semantic space
The term "Spanning the semantic space" was first coined by Osgood et al. The semantic range in this project is a space that expresses meanings such as expressing emotions (such as happy, sad, astonishing, etc.) or expressing perceived characteristics (such as familiar, strange, strange, precious, etc.).
The words in this step are presented in the form of adjectives and descriptive phrases and can describe the subject and content of this project. For this purpose, about one hundred words related to the content of the project have been selected so that after the analysis of the next step, a number of Kansei words can be obtained in the form of semantic differentiation.(The selection and survey of these words has been done in Persian. Now, after translating these words, the meaning and reason for choosing and concluding these words may seem different, which is due to the inevitable semantic differences between Persian and English.)
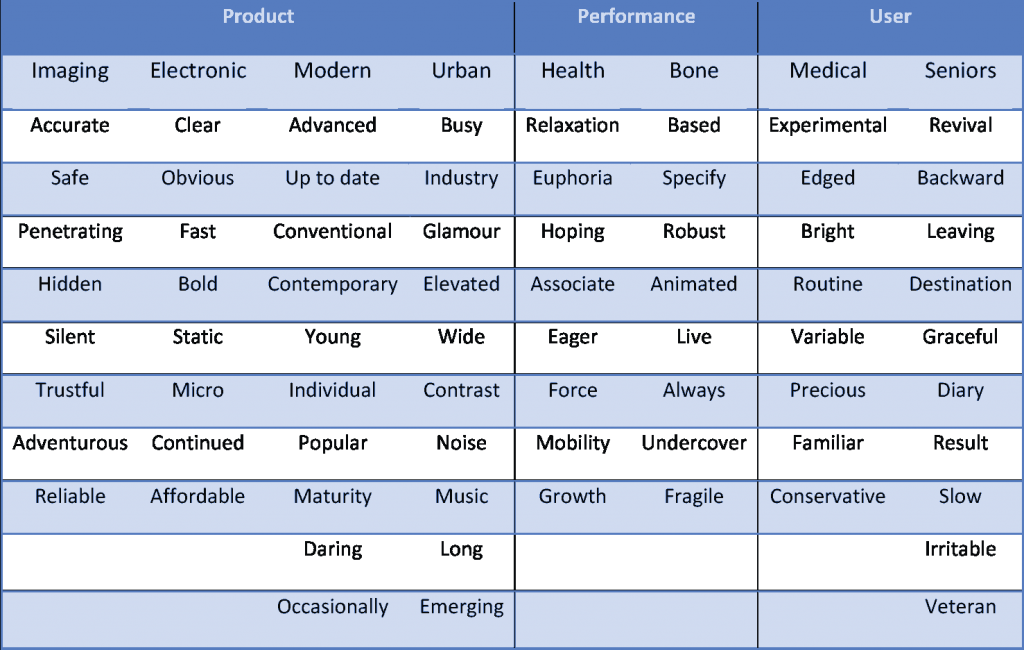
Span the semantic space
Domain of choice
Domain of choice includes "selecting a target group", "market position" and "whatever indicates the desired product".
From the users' point of view
1. Medical staff in the form of hospitals and clinics as product buyers
2. Radiologist or densitometer technician as the operating user
3. The patient as a non-active consumer
In terms of age
1. Children
2. Menopausal middle-aged
3. The elderly
4. Patients with bone diseases

Domain of choice
After collecting the semantic words, from each related word group, several non-synonymous words can be selected as Kansei words. These words can be examined in the form of binary sets of semantic differentiation or the 5 point Likert scale.
Thus, the selected words include these words:
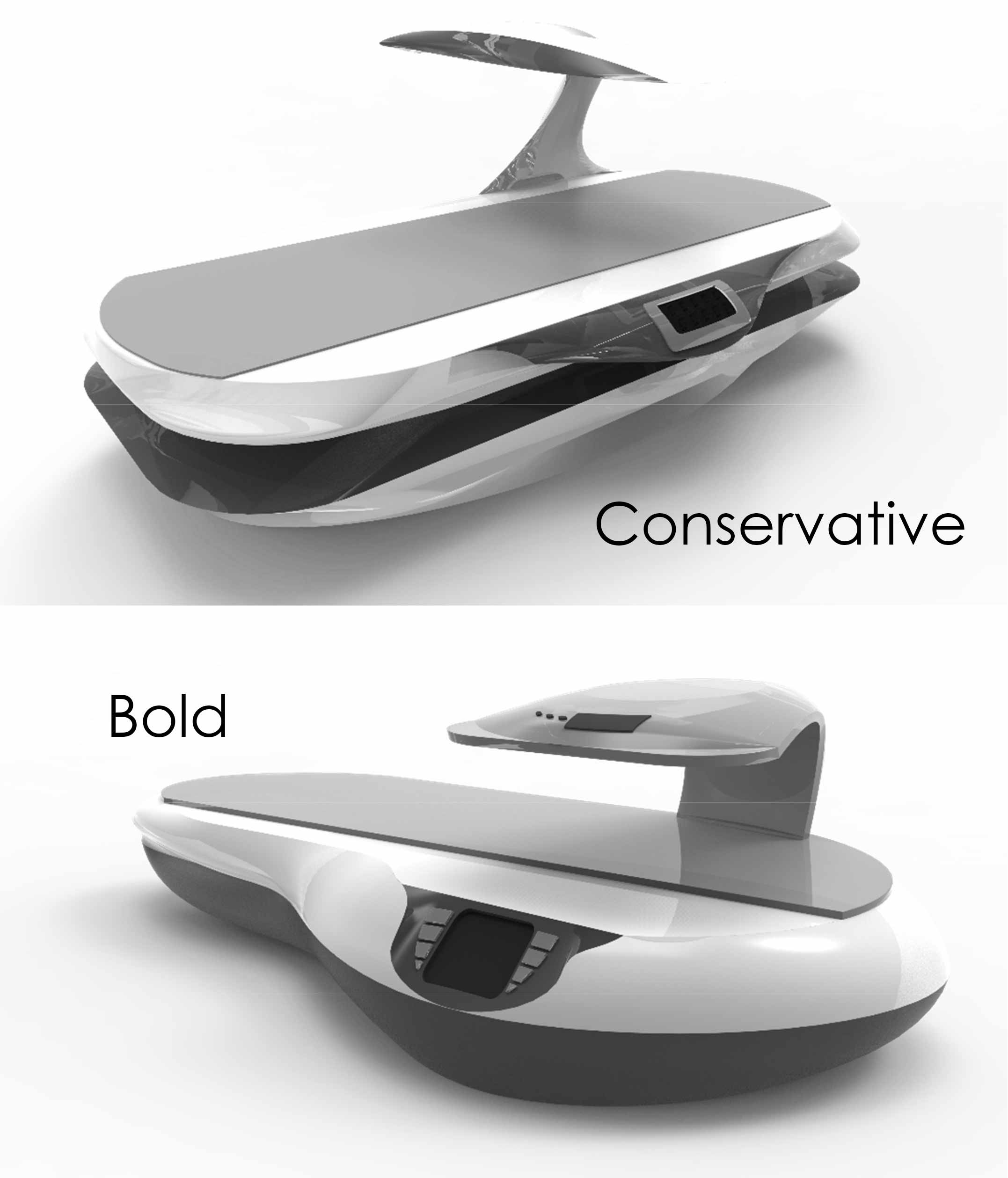
Hidden-obvious; Suspicious-sure; Wide-limited; History - Emerging; Hidden - evident; Everyday-occasional; Bold-conservative;
Stable-turbulent; Silent-Noisy; Continuous-interrupted; Brittle-strong; Precious-Affordable; Common - unfamiliar; Micro-macro;
Span the space of properties
In order to decide on the features and specifications of the product, these features must be segmented and describe the specifications of the product under descriptive headings. In this way, after collecting the required information from the product, unique and less repetitive features are separated in each product so that a relationship can be established between these features and the results obtained from the semantic domain. The following figure shows the steps to specify the range of product features.
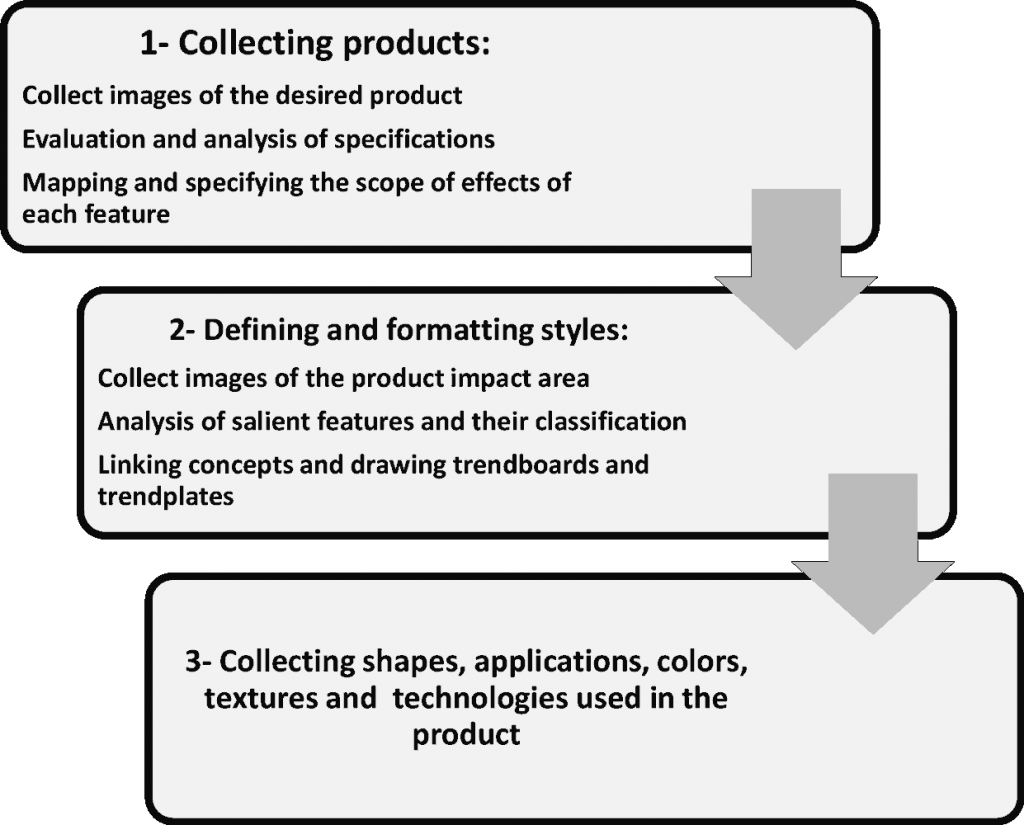
Span the space of properties
In order to achieve the product features, after collecting the product information, it is necessary to separate these features so that the selected products can be rated for these features. The table below illustrates this distinction:

Products and their features
Analysis ans Synthesis
After collecting the words and features, each product should be evaluated by users with Kansei words (previously prepared). Users must rate the desired words according to each product. After this evaluation, the results are collected and each feature is scored according to each product.
Then we have to find the relationship between the characteristics of the product and Kansei words, and after collecting these relationships, select the word that has the most relationship as the word used. For this purpose, design features are written in the vertical column (each feature is highlighted in only one product). Then, to select the Kansei words score, use the product numbers that have the desired feature, and at the end, these scores will be aggregated.
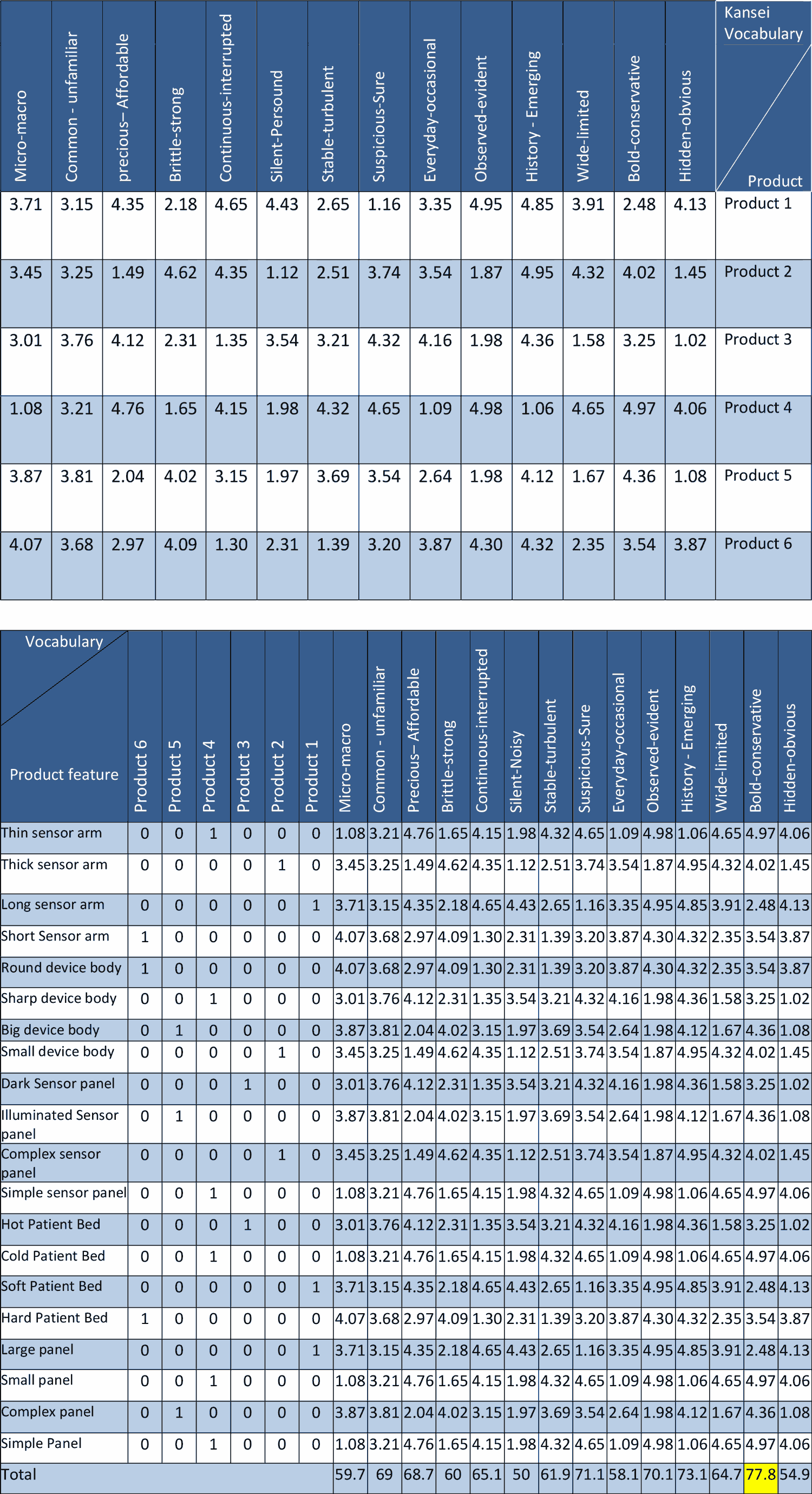
Relationship between product features and Kansei words
the Result
The words selected in this project are bold-conservative. Now it is time to design based on these words. The design should express these attributes. At the same time, the technical features related to these traits must be achieved. This relationship is an important part of design based on the Kansei/Affective method.
In contrast to the previous method, this method is expected to be more successful in innovation. While the previous method was more based on examining problems to reach a solution. This difference in the two methods, in addition to leading to two different results, can indicate the complementary role of the two methods together to design a single product. Which should be addressed in a separate project.


